Congratulations to QIAL’s Dr. Alexandra Badea and Dr. Trong-Kha Truong on receiving the 2025 Medical Physics Fall Seed Grant Award for their project, “Predictive Modeling of Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Using Explainable AI and High-Resolution MRI.”
Congratulations to QIAL’s Dr. Alexandra Badea and Dr. Trong-Kha Truong on receiving the 2025 Medical Physics Fall Seed Grant Award for their project, “Predictive Modeling of Alzheimer’s Disease Risk Using Explainable AI and High-Resolution MRI.”

Using photon-counting CT and deep learning, we show that voluntary exercise significantly mitigates high-fat diet–induced cardiac dysfunction in adult APOE-targeted mice, with the strongest benefits observed in APOE4 and humanized innate immune (HN) backgrounds.

Exercise mitigates high-fat diet–induced cardiac dysfunction via APOE genotype- and immune-dependent mechanisms: a photon-counting CT study in adult mice. Nadkarni R., Allphin A. J., Clark D. P., Qi Y., Han Z. Y., Ghaghada K. B., Badea A., Badea C. T. PLOS ONE, 2025. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0339293
How do genetics, sex, and immune signaling shape bone health as mice age?
Our study shows that photon-counting CT in APOE mouse models reveals strong sex- and immune-dependent bone loss, with female HN mice showing the most pronounced decline.
Nadkarni, R.; Han, Z.Y.; Allphin, A.J.; Clark, D.P.; Badea, A.; Badea, C.T.
Photon-Counting Micro-CT for Bone Morphometry in Murine Models.
Tomography 2025, 11, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography11110127

Delighted to host Dr. Kristina Bliznakova, Fulbright Scholar, at Duke’s Quantitative Imaging & Analysis Lab. Looking forward to teaming up on photon-counting CT and virtual imaging.

New article and three institutions collaborating!
We identify network biomarkers of Alzheimer’s risk by combining high-res MRI with multifactorial analysis in ApoE mouse models. Joint volume + texture patterns reveal how genotype, sex, diet, & immunity interact to shape brain networks.
Bridgeford EW, Chung J, Anderson RJ, Mahzarnia A, Stout JA, Moon HS, Han ZY, Vogelstein JT, Badea A : Network biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease risk derived from joint volume and texture covariance patterns in mouse models. PLoS One 20(8): e0327118. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0327118
Our team developed anatomically variable digital Wistar rat phantoms for realistic preclinical imaging simulations, enabling PCCT studies & reducing animal use.

Segars, H. E., Nadkarni, R., Badea, C. T., Badea, A., Chin, B., Johnson, G. A., Payne, J., Samei, E., & Segars, W. P. (2025). Development of anatomically variable digital Wistar rat phantoms for small animal imaging research. Medical Physics, 52(8), e18057. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.18057
Could your sense of smell reveal Alzheimer’s risk years before memory loss?
Our new study connects olfactory behavior, brain networks, & blood gene signatures to early AD vulnerability.
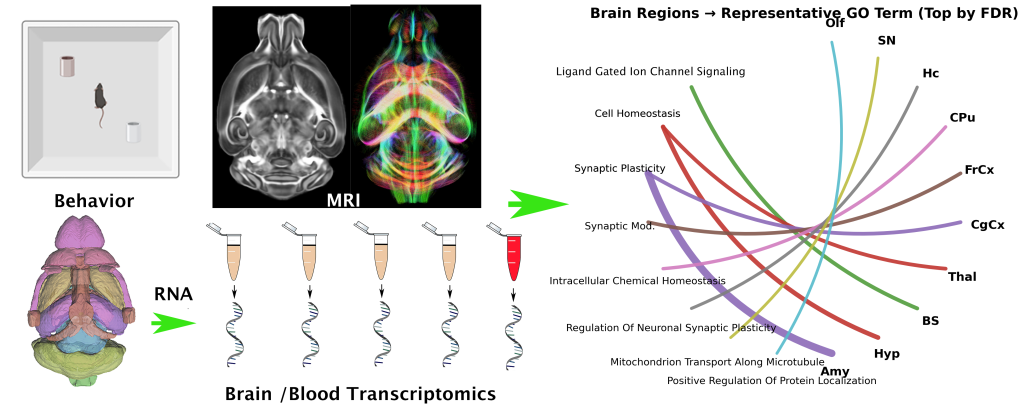
Moon, H.S.; Han, Z.Y.; Anderson, R.J.; Mahzarnia, A.; Stout, J.A.; Niculescu, A.R.; Tremblay, J.T.; Badea, A. Olfactory-Guided Behavior Uncovers Imaging and Molecular Signatures of Alzheimer’s Disease Risk. Brain Sci.2025, 15, 863. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080863
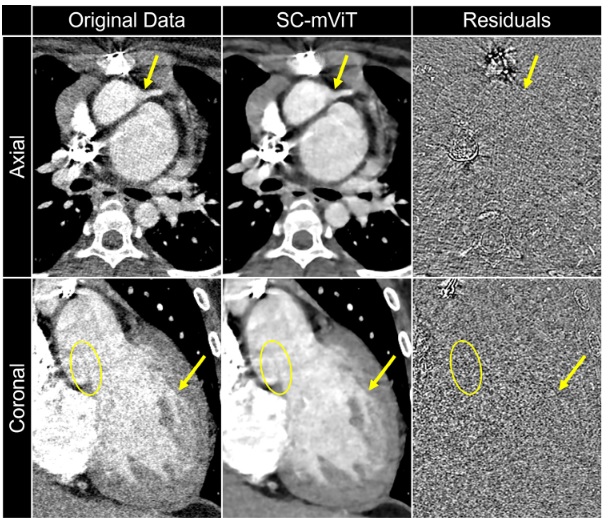
We developed a data-adaptive, self-supervised deep learning method combining sparse coding (SC) + visual transformer (ViT) for denoising pediatric cardiac photon-counting CT. Preserves anatomy, adapts to noise, generalizes well—even to preclinical data.
Clark, D. P., Cao, J. Y., & Badea, C. T. (2025). Denoising pediatric cardiac photon-counting CT data with sparse coding and data-adaptive, self-supervised deep learning. Medical Physics. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.17918
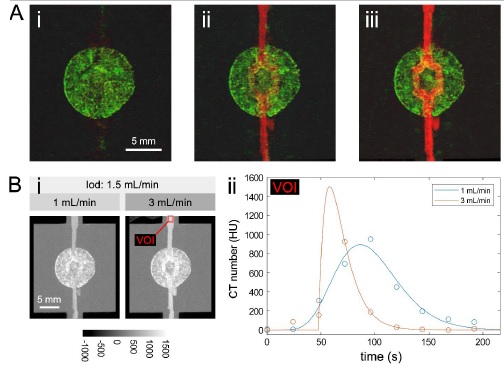
Our team developed a CT-visible bioprinted vascular patch using dual-contrast bioinks. Photon-counting CT enabled precise tracking of structure and perfusion, highlighting the role of imaging in cardiac repair.
Gil, C. J., Allphin, A. J., Jin, L., Salar Amoli, M., Rezapourdamanab, S., Tomov, M. L., Hwang, B., Sridhar, V., El Shammas, L. R., Wu, Y., Evans, C. J., Li, L., Singh, Y., Nandwani, R. K., Nish, J., Shen, M., Mahmoudi, M., Bauser, H. D., Pourmorteza, A., Roeder, R. K., Badea, C. T., & Serpooshan, V. (2025). Image-guided cardiac regeneration via a 3D bioprinted vascular patch with built-in CT visibility. Chemical Engineering Journal, 475, 165926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.165926
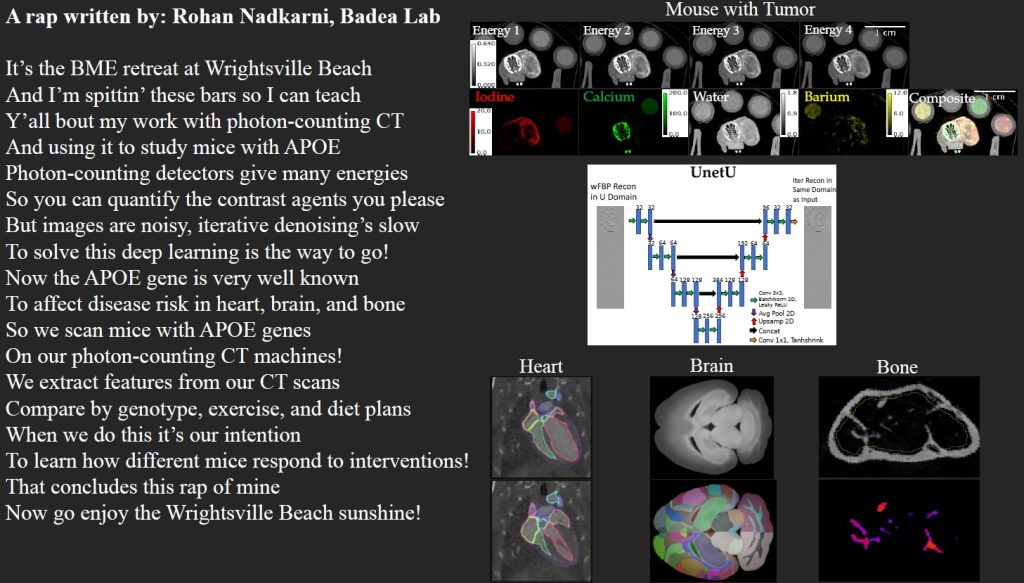
Our QIAL lab member Rohan Nadkarni brought the heat at the BME retreat—taking 2nd place in the rapid-fire challenge with original rap lyrics