PPT ESA Ordering Guide for Epic
PPT IV Iron Ordering Guide for Epic
Definition of Anemia in CKD
- <13 g/dL in males (<13.5 in non-CKD)
- <12 g/dL in females (<11.5 in non-CKD)
Causes of Anemia in CKD
- EPO Deficiency
- Functional Iron Deficiency (have adequate iron stores but iron cannot be mobilized)
- Absolute Iron Deficiency
| Absolute Iron Deficiency | Functional Iron Deficiency |
| TSAT<20 | TSAT <20 |
| Ferritin <100 | Ferritin >100 if CKD, >200 if ESKD on KRT |
How often to monitor for anemia?
- Every visit in patients with CKD stages 3-5
- Monthly if on KRT
- Check CBC with diff, reticulocyte count, serum iron, serum ferritin, TSAT, in select patients, can check B12 and folate if at risk for deficiency
Work-up of anemia
- If patient already on iron and ESA and not responding or anemia seems out of proportion to their CKD, will need further investigation, such as colonoscopy, workup of possible bone marrow malignancy and potentially hematology referral
- If iron deficient assess for causes of Iron deficiency, ask about GI losses and diet
Treatment Goals
- Adult patient with CKD not on dialysis:
- Hemoglobin >10 g/dL do not initiate EPO, can check iron studies and replete if iron deficient, rule out other causes of anemia
- If hemoglobin <10 g/dL can consider ESA, and treat iron deficiency if deficient. If TSAT ≤30 percent and/or a serum ferritin concentration ≤500 ng/mL, start on iron.
- Start ESAs if hemoglobin <10 g/dL if iron deficient and did not respond to iron supplementation alone
Iron Therapy:
| KDIGO Clinical guidelines for the use of iron to treat iron deficiency anemia | ||
| Patient Population | Threshold for therapy | Recommended Therapy |
| CKD with anemia not on ESA or Iron | An increase in Hgb concentration without starting ESA desired
TSAT is </30% and ferritin is </500ng/mL |
Trial of IV iron in patients on KRT
If not on KRT can try oral iron for 1-3 months, if ineffective or side effects can try IV iron |
| CKD with anemia on ESA but not Iron | An increase in hemoglobin concentration or decrease in ESA dose is desired
TSAT is </30% and ferritin is </500 ng/mL |
|
Oral Iron
- Daily dosing– Daily administration with goal elemental irοn intake of approximately 200 mg per day in up to three divided doses. Recommended by KDIGO. Can use ferrous sulfate 325mg, which is 65mg of elemental iron, three times daily.
- Alternate-day dosing– Alternate-day administration with goal elemental irοո intake of approximately 65 mg per day in a single dose, some data showing better absorption and fewer side effects but studies not done in patients with CKD
- Oral irοn should be administered between meals. Antacids may decrease efficacy, if on antacid recommend separating the antacid and iron supplement (i.e. one in AM and one in PM)
- Fеrriϲ citrate and sucroferric oxyhydroxide are oral phosphate binders that may be useful for oral irοn supplementation in patients who also have hyperphosphatemia. They are very expensive.
- Watch out for and be ready to treat constipation.
Consider using Intravenous Iron if
PPT ESA Ordering Guide for Epic
- Severe irоn deficiency (TSAT <12 %)
- Severe anеmiа (hemoglobin </7 g/dL) in asymptomatic patients
- Side effects to oral iroո
- Not responding to oral iron
- There are other IV iron formulations aside from listing below. Main one to remember is ferric carboxymaltose as it causes hypophosphatemia (usually seen in non-CKD).
| IV iron formulations | Elemental Iron (mg/ml) | Dosing | Side Effects |
| Ferrlecit (Sodium ferric gluconate) | 62.5 | 125 mg for 8 doses | Flushing, HA, fever, chills, hypotension |
| Venofer (Iron sucrose) | 20 | 100 mg for 10 doses | Flushing, HA, fever, chills, hypotension |
| Ferahame (Ferumoxytol) | 39 | 510 mg; 2 doses 3 to 8 days apart | Flushing, HA, fever, chills, hypotension |
| INFed (Dextran) | 50 | 25mg IV once, then wait 30min to ensure no reaction, if no reaction give remaining 975mg one time. Alternatively can use formula to calculate precise dose. | Test dose used. Can cause severe allergic reaction |
| *Ferrlecit or InFed (dextran) is preferred at duke. InFed is a one time dose but can cause severe allergic reactions. Ferrlecit is over 8 doses but less likely to cause a reaction. | |||
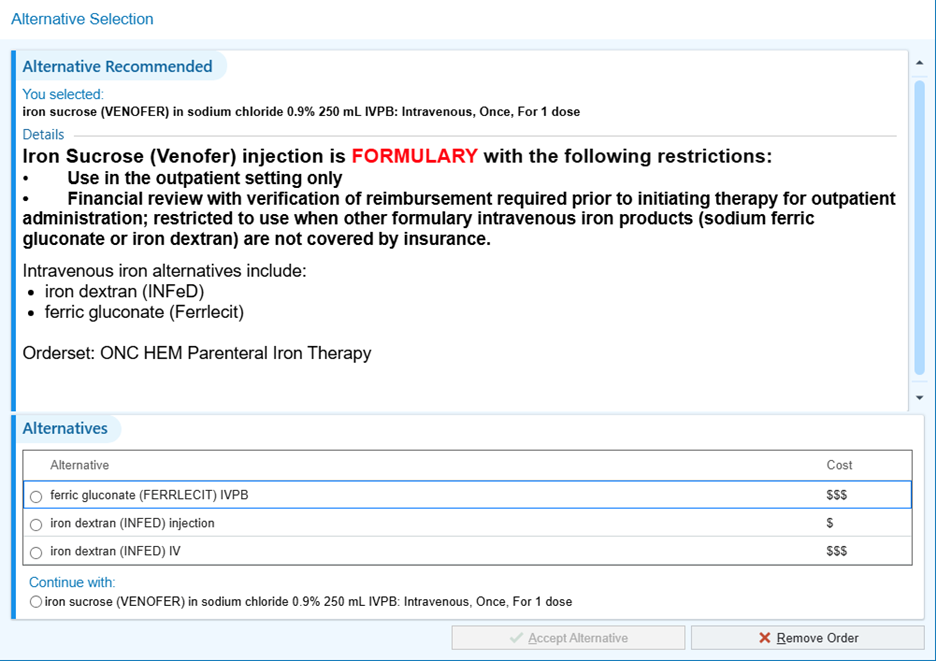
ESAs
PPT ESA Ordering Guide for Epic
- Micera (methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta) is the longest acting, Darbapoetin is longer acting than Epoetin
- Avoid use of ЕЅAѕ in patients with active malignancy if possible due to increase in the risk of progression or recurrence of cancer.
- Avoid EЅAѕ in patients with history of stroke since they may be at a higher risk for adverse effects (eg, recurrent stroke) from ЕЅΑs.
- Increased risk of blood clots with ESA.
- EPO resistance if failure to achieve a hemoglobin >11 g/dL despite an epoetin dose >300-450 units/kg/week or the equivalent of another ESA. Investigate for other causes of anemia if a patient has EPO resistance. Ensure the patient is iron replete.
| ESA formulation | Dosing |
| Darbapoetin | IV or SubQ 0.45mcg/kg every 2-4 weeks.
|
| Micera
(Methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta) |
Subq 0.6mcg/kg every 2 weeks or 1.2mcg/kg monthly
IV 0.6mcg/kg every 2 weeks
|
| Epoetin | IV or Subq 50-100U/kg every 1-2 weeks |
| *Only Epoetin and darbepoetin are available to order at the Duke infusion center. | |
Excel document to convert between ESAs
Edited by Aruna Phekoo and Matthew A. Sparks Aug 12, 2025



































































































































































































