2021
- Sherwood, D.R. (2021). Basement membrane remodeling guides cell migration and c
 ell morphogenesis during development. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. pdf
ell morphogenesis during development. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. pdf
- Garde, A. and Sherwood, D.R. (2021). Fueling cell invasion through extracellularmatrix. Trends in Cell Biology. Jun;31(6):445-456. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2021.01.006. pdf
2020
- Gordon, K.L., Zussman, J.W., Li, X., Miller, C., Sherwood, D.R. (2020). Stem cell niche exit in C. elegans via orientation and segregation of daughter cells by a cryptic cell outside the niche. eLife 2020;9:e56383 DOI: 10.7554/eLife.56383. pdf
- Keeley, D.P., Hastie, E., Jayadev R., Kelley, L.C., Chi, Q., Payne, S.G., Jeger, J.L., Hoffman, B.D., Sherwood, D.R. (2020). Comprehensive endogenous tagging of
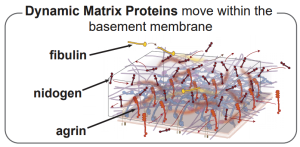 basement membrane components reveals dynamic movement within the matrix scaffolding. Dev Cell. pdf
basement membrane components reveals dynamic movement within the matrix scaffolding. Dev Cell. pdf
- Lin MH, Pope BD 3rd, Sasaki T, Keeley DP, Sherwood DR, Miner JH. Mammalian hemicentin 1 is assembled into tracks in the extracellular matrix of multiple tissues. Dev Dyn. 2020;249(6):775-788. doi:10.1002/dvdy.159 pdf
2019
- Hastie E., Sellers R., Valan B., Sherwood D.R. (2019) A scalable CURE Using a CRISPR/Cas9 Fluorescent Protein Knock-In Strategy in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2019 Dec 18;20(3):20.3.60. pdf
- Jayadev R., Chi Q., Keeley, D.P., Hastie, E.L., Kelley, L.C.,Sherwood D.R. (2019) α-Integrins dictate distinct modes of type IV collagen recruitment to basement membranes. J. Cell Biol., Aug 6. pii cb.201903124. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201903124. pdf
- Hartman J.H., Richie C.T., Gordon K.L., Mello D.F.,, Castillo P., Zhu A., Wang Y., Hoffer B.J., Sherwood D.R., Meyer J.N.,, Harvey B.K. (2019). MANF deletion abrogates early larval Caenorhabditis elegans stress response to tunicamycin and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur J Cell Biol. May 21. pii: S0171-9335(18)30348-0. doi: 10.1016/ j.ejcb.2019.05.002. PMID:31138438. pdf
- Gordon K.L., Payne, S.G., Linden-High L.M., Pani, A.M., Goldstein, B
 .,Hubbard, J.A., Sherwood. D.R. (2019). Ectopic germ cells can induce niche-like enwrapment by neighboring body wall muscle. Curr Biol. Mar 4;29(5):823-833.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub .2019.01.056. Epub 2019 Feb 21.PMID: 30799241. pdf
.,Hubbard, J.A., Sherwood. D.R. (2019). Ectopic germ cells can induce niche-like enwrapment by neighboring body wall muscle. Curr Biol. Mar 4;29(5):823-833.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub .2019.01.056. Epub 2019 Feb 21.PMID: 30799241. pdf
- Kelley, L.C., Hastie E., Cáceres, R., Chi. Q., Schindler A.J., Jiang Y., Matus, D.Q., Julie Plastino J., and Sherwood, D.R. (2019).
 Adaptive F-actin polymerization and localized ATP production drive basement membrane invasion in the absence of MMPs. Dev Cell. Jan 23. pii: S1534-5807(18)31086-4. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.12.018 pdf
Adaptive F-actin polymerization and localized ATP production drive basement membrane invasion in the absence of MMPs. Dev Cell. Jan 23. pii: S1534-5807(18)31086-4. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.12.018 pdf
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology-Forcing Through Barriers
2018
- Cáceresa, R., Bojanalaa N., Kelley, L.C., Dreiere J., Manzia, J., Federicoa, F.D., Chi, Q., Rislera, T.,, Testae, I., Sherwood, D.R.,, Plastino, J. (2018). Forces drive basement membrane invasion in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Nov 6;115(45):11537-11542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1808760115. Epub 2018 Oct 22. PMID: 30348801. pdf
-
Hibshman J.D., Leuthner T.C., Shoben C., Mello D.F., Sherwood D.R., Meyer J.N., Baugh L.R. (2018). Non-selective autophagy reduces mitochondrial content during starvation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. Aug 22. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00109.2018. PMID:30133321 pdf
- Keeley D.P. and Sherwood D.R. (2018). Tissue linkage throug
 h adjoining basement membranes: The long and the short term of it. Matrix Biol. May 24. pii: S0945-053X(18)30190-2. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.05.009. [Epub ahead of print]. pdf
h adjoining basement membranes: The long and the short term of it. Matrix Biol. May 24. pii: S0945-053X(18)30190-2. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.05.009. [Epub ahead of print]. pdf
- Hartman J.H., Smith L. L., Gordon K.L., Laranjeiro R., Driscoll M.,Sherwood D.R., Meyer J.N. (2018). Swimming Exercise and Transient Food Deprivation in Caenorhabditis elegans Promote Mitochondrial Maintenance and Protect Against Chemical-Induced Mitotoxicity. (2018) Sci Rep. May 29;8(1):8359. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26552-9. pdf
-
Sherwood D.R. and Plastino J. (2018) Invading, Leading and Navigating Cell in Caenorhabditis elegans: Insights into Cell Movement In Vivo. Genetics Jan;208(1):53-78. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300082. pdf
2017
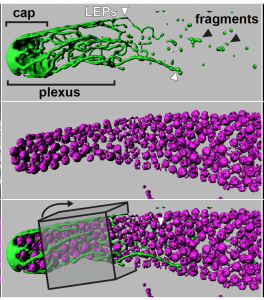
- Naegeli, K.M., Hastie, E.L., Garde, A., Wang Z., Keeley D.P., Gordon K.L., Pani A.M., Kelley L.C., Morrisey, M.A., Chi.Q., Goldstein.,B, Sherwood D.R. (2017). Cell invasion in vivo via rapid exocytosis of a transient lysosome-derived membrane domain. Dev Cell. Nov 20;43(4):403-417 pdf
- Linden, L.M., Gordon, K.L., Pani, A.M., Payne, S.G., Garde A., Burkholder, D., Chi Q., Goldstein, B., Sherwood, D.R. (2017). Identification of regulators of germ stem cell enwrapment by its niche in C. elegans. Dev Biol. Sep 1;429(1):271-284. doi: 10.1016/ j.ydbio. 2017.06.019. pdf
- Kelley, L.C., Wang, Z., Hagedorn, E.J., Wang, L., Shen W., Lei, S., Johnson, S.A.,, Sherwood, D.R. (2017). Live-cell confocal microscopy and quantitative 4D image analysis of anchor cell invasion through the basement membrane in C. elegans. Nat Protoc. Oct;12(10):2081-2096. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2017.093. pdf
- Jayadev R. and Sherwood D.R. (2017). Morphogenesis: Shaping Tissues through extracellular force gradients. Curr Biol. Sep 11;27(17):R850-R852. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.07.040. pdf
- Keeley, D.P., and Sherwood, D.R. (2017). Breaching and opening basement membrane barriers: the anchor cell leads the way. Extracellular matrix in tumor biology, pp 91-115 Springer Nature. pdf
- Jayadev R. and Sherwood D.R. (2017). Primer: Basement Membranes. Curr Biol. Mar 20;27(6):R207-R211. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.02.006. pdf
2016
- McClatchey, S.T.H., Wang Z., Linden, L.M., Hastie, E.L., Wang, L., Shen, W., Chen, A., Chi, Q., Sherwood, D.R. (2016). Boundary cells restrict dystroglycan trafficking to control basement membrane sliding during tissue remodeling. eLIFE. Sep 23;5. pii:
e17218. pdf
- Jayadev R. and Sherwood D.R. (2016). Sculpting Tissues by Fibrils. Dev Cell. Jul 11;38(1):1-3. pdf
- Hastie, E.L. and Sherwood, D.R. (2016). A new front in cell invasion: The invadopodial membrane. Eur J Cell Biol. 2016 Jun 24. S0171-9335(16)30105-4. pdf
- Morrissey, M.A., Jayadev, R., Miley, G.R., Blebea, C.A., Chi, Q., Ihara, S., Sherwood, D.R. (2016). SPARC promotes cell invasion in vivo by decreasing type IV collagen levels in the basement membrane. PLoS Genet. 12(2): e1005905. pdf
- Lohmer, L.L, Clay, M.R., Naegeli, K.M., Chi, Q., Ziel, J.W., Hagedorn, E.J., Park, J.E., Jayadev, R., Sherwood, D.R. (2016). A sensitized screen for genes promoting invadopodia function in vivo: CDC-42 and Rab GDI-1 direct distinct aspects of invadopodia formation. PLoS Genet.. Jan 14;12(1):e1005786. pdf
http://blogs.plos.org/biologue/2016/02/29/understanding-images-how-do-cells-make-invasive-feet/
2015

- Matus, D.Q., Lohmer, L.L., Kelley, L.C., Schindler, A.J., Korhman, A.Q., Barkoulas, M., Zhang, W., Chi, Q and Sherwood, D.R. (2015). Invasive cell fate requires G1 cell-cycle arrest and histone deacetylase-mediated changes in gene expression. Dev Cell. Oct. 26; 35, 162–174. pdf
-Developmental Cell Preview. An arresting story about basement membrane invasion. pdf
- Meeting Report-Imaging the Cell (2015). J. of Cell Sci. Nov. 1; 128(21): 3843-7. pdf
- Clay, M.R. and Sherwood D.R. (2015). Basement Membranes in the Worm: A Dynamic Scaffolding that Instructs Cellular Behaviors and Shapes Tissues. Current Topics in Membranes. Sep 12; 76:1-37. pdf
- Zou, W., Yadav, S., Devault, L., Jan, Y.N., Sherwood, D.R. (2015). RAB-10-dependent membrane transport is required for dendritic arborization”. PLOS Genet. Sep 22; 11(9): e1005484. pdf
- Sherwood, D.R. (2015). A developmental biologists “outside-the-cell” thinking. J. Cell Biol. Aug 3; 210(3): 369-372. pdf
- Wei, X., Howell, A.S., Dong, X., Taylor, C.A., Cooper, R.C., Zhang, J., Zou, W., Sherwood, D.R., Shen, K. (2015). The unfolded protein response is required for dendrite morphogenesis. eLIFE, 4:e06963. pdf
- Morrissey, M. A. and Sherwood, D.R. (2015). An active role for basement membrane assembly and modification in tissue sculpting. J. Cell Science, 128, 1–8 doi:10.1242/jcs.168021. pdf
2014
- Schindler, A.J. and Sherwood, D.R. (2014). Should I stay or should I go? Identification of novel nutritionally regulated developmental checkpoints in C. elegans. Worm 3:4, e979658. pdf
- Armenti, S.T., Lohmer, L.L, Sherwood, D.R., and Nance, J. (2014). Repurposing an endogenous degradation system for rapid and targeted depletion of C. elegans proteins. Development. 141:1-8 doi.1242/dev.115048. pdf

- Morrissey, M. A., Hagedorn, E. J., McClatchey, S. T. H., Chi, Q., Hall, D. H., Sherwood, D. R. (2014). B-Link: A hemicentin, plectin, integrin-dependent adhesion system that links tissues by connecting adjacent basement membr
anes. Dev Cell. Nov 10; 31(3): 319-331. pdf supplemental info
- Wang, L., Shen, W., Lei, S., Matus, D., Sherwood, D., Wang, Z. (2014). MIG-10 (Lamellipodin) stablizes invading cell adhesion to basement membrane and is a negative transcriptional target of EGL-43 in C. elegans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Sep 26;452(3):328-33. pdf
- Wang, Z., Linden, L., Naegeli, K., Ziel, J. W., Chi, Q., Hagedorn, E. J., Savage, N. S.,Sherwood, D. R. (2014). UNC-6 (netrin) stabilizes oscillatory clustering of the UNC-40 (DCC) receptor to orient polarity. Journal of Cell Biology Sep 1;206(5):619-
 33. pdf
33. pdf
-In focus feature by Ben Short at JCB:pdf
-Duke today: Scientist Uncover Navigation System
-Dispatch, Current Biology 3 November 2014, 24(21):R1050-2. pdf
- Matus, D. Q., Chang, E., Makohon-Moore, S., Hagedorn, M., Sherwood, D. R. (2014). Cell division and targeted cell cycle arrest opens and stabilize
 s basement membrane gaps. Nature Commun. Jun 13;(5):4184. pdf supplemental materials
s basement membrane gaps. Nature Commun. Jun 13;(5):4184. pdf supplemental materials
- Schindler, A. J., Baugh, L. R., Sherwood, D. R. (2014). Identification of late larval stage developmental checkpoints in Caenorhabditis elegans regulated by Insulin/IGF and steroid hormone signaling pathways. PLoS Genet. Jun 19;10(6):e1004426. pdf
- Lacroix B., Bourdages K. G., Dorn J. F., Ihara S., Sherwood D. R., Maddox P. S., Maddox A. S. (2014). In situ imaging in C. elegans reveals developmental regulation of microtubule dynamics. Dev Cell. Apr 28; 29(2):203-16.
- Lohmer, L. L., Kelley, L. C., Hagedorn, E. J., Sherwood, D. R. (2014). Invadopodia and basement membrane invasion in vivo. Cell Adh Migr.;8(3):246-55. pdf
 Hagedorn E. J*., Kelley, L. C*., Naegeli, K. M., Wang, Z., Chi, Q., Sherwood, D.R. (2014). ADF/cofilin promotes invadopodial membrane recycling during cell invasion in vivo. J Cell Biol. Mar 31; 204(7): 1209-18. pdf
Hagedorn E. J*., Kelley, L. C*., Naegeli, K. M., Wang, Z., Chi, Q., Sherwood, D.R. (2014). ADF/cofilin promotes invadopodial membrane recycling during cell invasion in vivo. J Cell Biol. Mar 31; 204(7): 1209-18. pdf - *These authors contributed equally
- Wang, Z., Chi, Q., Sherwood, D.R. (2014). MIG-10 (Lamellipodin) has netrin independent functions and is a FOS-1A transcriptional target during anchor cell invasion in C. elegans. Development. 141:134-1353. pdf
- Kelley, L. C., Lilley-Lohmer, L., Hagedorn, E. J., Sherwood, D. R. (2014). Traversing the basement membrane in vivo: a diversity of strategies. Journal of Cell Biology. 204 (3). 291–302. pdf
2013
 Hagedorn E. J., Ziel J.W., Morrissey M. A., LindenL.M., Wang Z, Chi Q, Johnson S. A., Sherwood, D. R. (2013). The Netrin Receptor DCC Focuses Invadopodia Driven Basement Membrane Transmigration in vivo. Journal of Cell Biology, 10; 201(6): 903-13. pdf
Hagedorn E. J., Ziel J.W., Morrissey M. A., LindenL.M., Wang Z, Chi Q, Johnson S. A., Sherwood, D. R. (2013). The Netrin Receptor DCC Focuses Invadopodia Driven Basement Membrane Transmigration in vivo. Journal of Cell Biology, 10; 201(6): 903-13. pdf
- Morrissey, M. A., Hagedorn, E. J., Sherwood D. R. (2013). Cell Invasion through basement membrane: The netrin receptor DCC guides the way. Worm 2 (3) e26169-1-6. pdf
- Schindler Adam J., Sherwood David R. (2013). Morphogenesis of the Caenorhabditis elegans vulva. WIREs Dev Biol. 2(1):75-95. pdf
2011
- Hagedorn, E.J. and Sherwood, D. R. (2011). Cell Invasion Through Basement Membrane: The Anchor Cell Breaches the Barrier. Curr Opinion Cell Biol. 23(5): 589-9. pdf
- Schindler, A.J. and Sherwood, D.R. (2011). The transcription factor HLH2/E/Daughterlessregulates anchor cell invasion in C. elegans. Dev. Biol. Sep 15;357(2):380-91. pdf
- Hagedorn, E.J. and Sherwood, D.R., Cell Picture Show, Cell Motility (2011). “WalkingThrough Walls”. http://www.cell.com/pictureshow/cell-motility
- Wang, Z., and Sherwood, D.R. (2011). Dissection of Genetic Pathways in C. elegans. Molecular Genetics and Development – Methods in Cell Biol. 106:113-57. pdf
- Ihara, S., Hagedorn, E.J., Morrissey, M.A., Motegi, F., Kramer, J.M., Sherwood, D.R., (2011) Basement membrane sliding and targeted adhesion remodels tissue boundaries during uterine-vulval attachment in C. elegans. Nat Cell Biol. Jun;13(6):641-51. pdf
-Dispatch, Current Biology 9 August 2011, 21(15):R585-7. pdf
2010
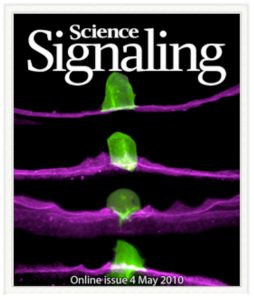
- David Q. Matus, David R. Sherwood, and Annalisa M. VanHook PODCAST Sci Signal.,11 (2010) 3, Issue 121, p. pc10. Science Signaling Podcast_ 11 May 2010
- Matus, D.Q., Li, X-Y., Durbin S., Agarwal, D., Chi, Q., Weiss, S.J., Sherwood, D.R. (2010). Identification of novel regulators of cell invasion across basement membrane in vivo. Sci Signal. 4:3(120): ra35. pdf supplemental material
-Science, Editors Choice, 28 May 2010, p. 1077. pdf
-Research Highlights in Nature Reviews Cancer, 27 May 2010; doi 10. 1038/nrc 2878. pdf
- Ziel, J.W., Sherwood, D.R. (2010). Roles for Netrin Signaling Outside of Axon Guidance: A View from of Worm. Dev Dyn 239(5): 1296-305. pdf
2009
- Hagedorn, E.J., Yashiro, H., Ziel, J.Z., Ihara, S., Wang, Z., and Sherwood, D.R. (2009). Integrin Acts Upstream of Netrin Signaling to Regulate Formation of the Anchor Cell’s Invasive Membrane in C. elegans. Dev. Cell 17, 187-198. pdf
-Comment in Dev Cell. Integrins Anchor the Invasive Machinery (2009), 17(2): 158-60. pdf
- Ziel, J.W., Matus, D.Q., Sherwood, D.R. (2009). An expression screen for RhoGEF genes involved in C. elegans gonadogenesis., Gene Expr Patterns 9(6): 397-403. pdf
- Sherwood, D.R. (2009) David Sherwood: invasive procedures. Interview by Ben Short., J. Cell Biol, 185(4): 568-9. pdf

- Ziel, J.W., Hagedorn, E.J., Audhya, A., Sherwood, D.R. (2009) UNC-6 (netrin) orients the invasive membrane of the anchor cell in C. elegans., Nat Cell Biol. 11(2): 183-9. pdf
- Sherwood, D. R. (2006). Cell invasion through basement membranes: an anchor of understanding. Trends Cell Biol. 16(5): 250-256. pdf
- Sherwood, D. R., Butler, J.A., Kramer, J.M., and Sternberg, P.W. (2005). Fos-1 promotes basement-membrane removal during anchor-cell invasion in C. elegans. Cell 121, 951-962. pdf Supplemental Data
-Comment in: Cell. 2005 Jun17; 121(6): 816-7. pdf
-Editorial in: Matrix Biology. 2006; 25(1):1-2.
- Sherwood, D. R., and Sternberg, P.W. (2003). Anchor cell invasion into the vulval epithelium in C. elegans. Dev. Cell 5, 21-31. pdf
-Comment in: Dev Cell. 2003 Jul; 5(1):5-7. pdf
- Inoue, T., Sherwood, D. R., Aspöck, G., Butler, J. A., Gupta, B. P., Kirouac, M., Wang, M., Lee, P.-Y., Kramer, J. M., Hope, I., Burglin, T.R., Sternberg, P.W. (2002). Gene expression markers for Caenorhabditis elegans vulval cells. Mech. Dev. 119S, S203-S209.
- Palmer, R.A., Inoue, T., Sherwood, D.R., Jing, L.I., and Sternberg, P.W. (2002) Caenorhabditis elegans cog-1 locus encodes a GTX/Nkx6.1 homeodomain proteins and regulates multiple aspects of reproductive system development. Dev. Biol. 252, 202-213.