Team: Oral Surveillance, aka the “EMEUNET Fencers”
Authors: the EMEUNET Group
- Ertugrul Cagri Bolek, MD, MSC, Rheumatologist, Etlik City Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
- Claudia Cobilinschi, MD, PhD, Rheumatologist Sf. Maria Clinical Hospital, Assistant Lecturer, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania
- Kim Lauper, PD Dr med. Consultant and Senior Clinical Associate, Division of Rheumatology, Geneva University Hospitals & Faculty of Medicine, University of Geneva, Switzerland
- Tue Wenzel Kragstrup, MD, PhD, Associate Professor Aarhus University, Denmark
Team Overview
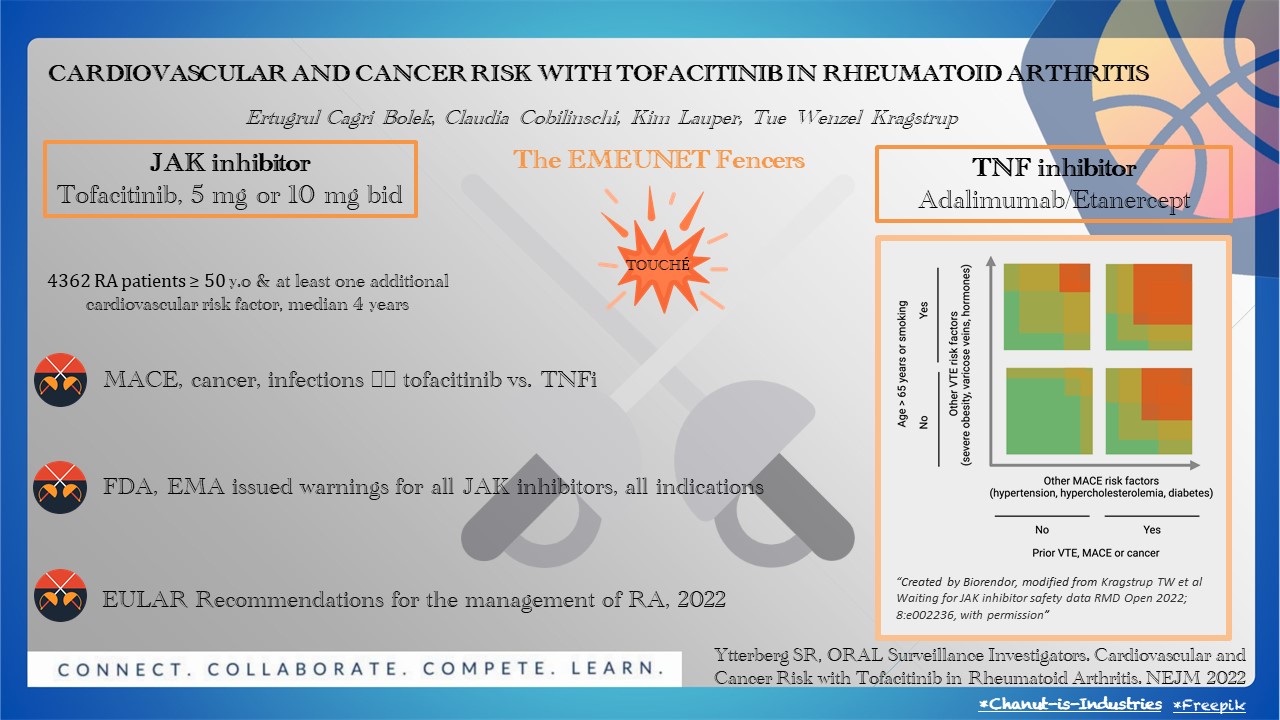
Fencing requires two agile participants, elegantly competing and scoring points when touching the opponent. Likewise, the ORAL Surveillance article brings to the piste tofacitinib, the JAK inhibitor (JAKi) (5 mg or 10 mg twice daily), and subcutaneous TNF inhibitors (adalimumab or etanercept). The duel, a randomized, open-label, post-authorization trial, is set out to determine the cardiovascular and cancer risk linked to tofacitinib.
Four thousand three hundred sixty-two patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) of 50 years or older and with at least one additional cardiovascular risk factor were randomly assigned as referees. They lifted a red card whenever major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE, death from cardiovascular causes, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke) and cancers, excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer, occurred. La riposte took a median of four years. It revealed that the incidences of MACE and cancer were higher with the combined tofacitinib doses (3.4% and 4.2%, respectively) than with a TNF inhibitor (2.5% and 2.9%). Serious infections were more frequent with high doses of tofacitinib, as were herpes zoster and tuberculosis. Touché! Tofacitinib parried the ongoing attack by showing non-inferiority criteria with early and sustained disease remission.
Fencing is derived from the Latin “defensa” which means protection. The FDA and EMA jury issued warnings for all JAK inhibitors, expanding the risk above to all drug indications. This further led to a change in RA recommendations, impacting the worldwide prescription of the JAKi and previous RA concepts of disease control and treat-to-target.
The EMEUNET Fencers team thrives on the “All for one and one for all” motto. So we wrap up with a brave “En garde!” for our competitors.
Want to learn more?
See the Q&A on theMednet.org about the following question: What role do you see for JAK inhibitors in RA treatment strategies given the data we now have regarding CV and cancer outcomes?
Back to the full list of scouting reports.