Contents
- 1 Translating structure-function to therapeutics:
- 1.1 1. What are the molecular mechanisms of ion and lipid transport across cell membranes?
- 1.2 2. How do ion and lipid transport systems regulate health and contribute to disease?
- 1.3 B. Calcium-activated lipid scramblases
- 1.4 3. How can we target ion and lipid transport pathways for therapeutic development?
- 1.5 4. Method development
Translating structure-function to therapeutics:
1. What are the molecular mechanisms of ion and lipid transport across cell membranes?
A. Calcium-activated chloride channels
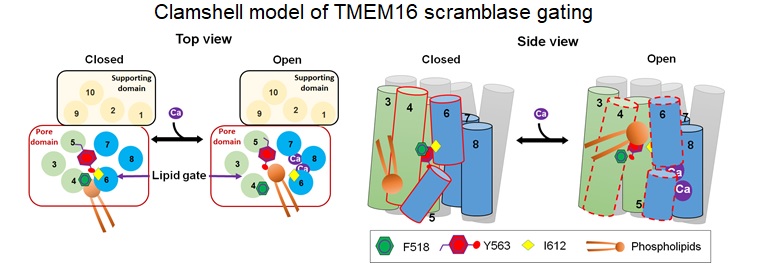
- The structural basis of the calcium-dependent activation of TMEM16 proteins (Tien, et al, eLife, 2014)

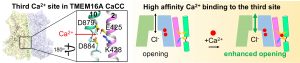
- The third calcium binding site that allosterically regulates TMEM16A activation (Le and Yang, Cell Reports, 2020)
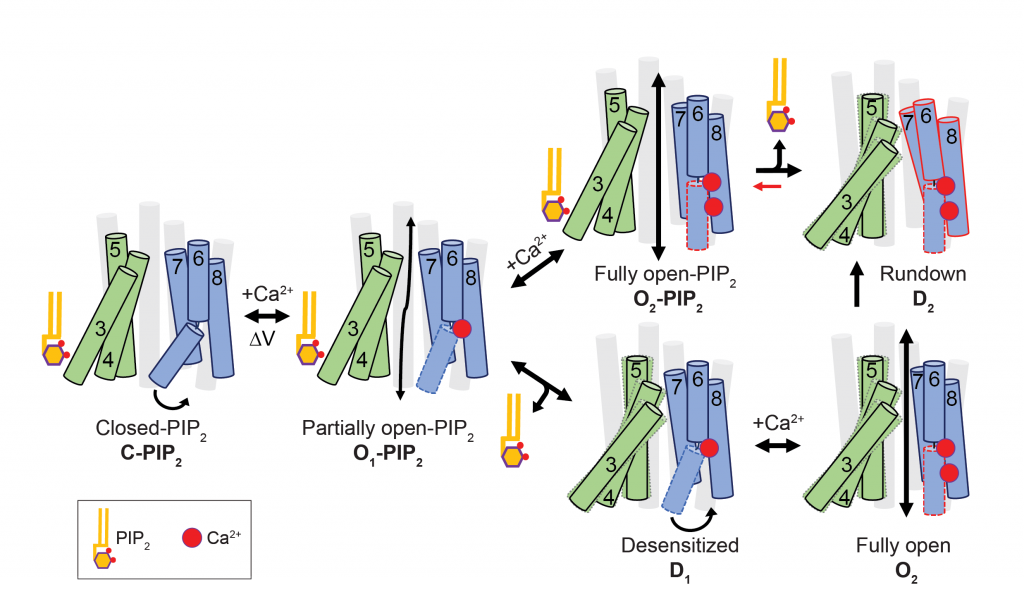
- Elucidated the molecular basis of TMEM16A channel desensitization and the modular design of TMEM16 proteins (Le, et al, Nat. Commun., 2019)
B. Calcium-activated lipid scramblases
- Discovered an activation gate that controls TMEM16 lipid and ion transport (Le, et al, Nat. Commun., 2019)
- Subdued is a new calcium-activated lipid scramblase with non-selective channel functions in Drosophila (Le, et al, JBC, 2019)
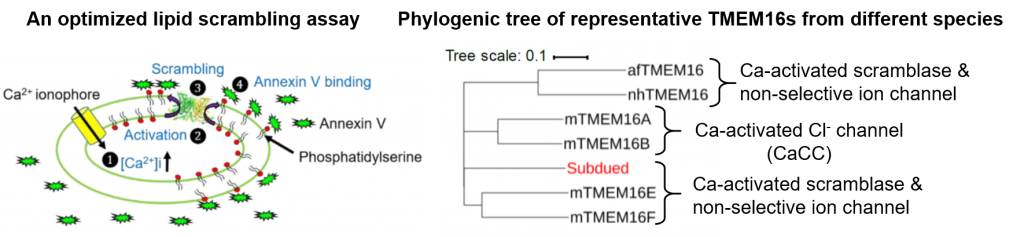
- Uncovered the mechanism of pH regulation of TMEM16 scramblases and channels. (Liang and Yang, J. Gen. Physiol. 2020). See Commentary here.

C. Other Transmembrane Channel-Scramblase (TCS) superfamily members
- Discovered evolutionarily conserved lipid scrambling potential of TCS super family members, most of which were considered as pure ion channels. Engineered first mechano-sensitive lipid scramblases. (Lowry, AJ et al, eLife, 2024)

2. How do ion and lipid transport systems regulate health and contribute to disease?
A. Calcium-activated chloride channels
- TMEM16B as an overlooked calcium-activated chloride channel mediates cerebellar motor learning (Zhang, et al, Neuron, 2017)
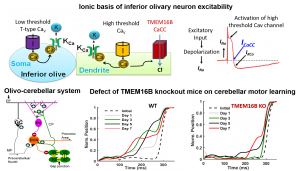
- Calcium channels and calcium-activated chloride and potassium channels mediate a novel inhibitory mechanism for the excitability of medial habenular neurons (Kawai, Sci. Adv. 2025).
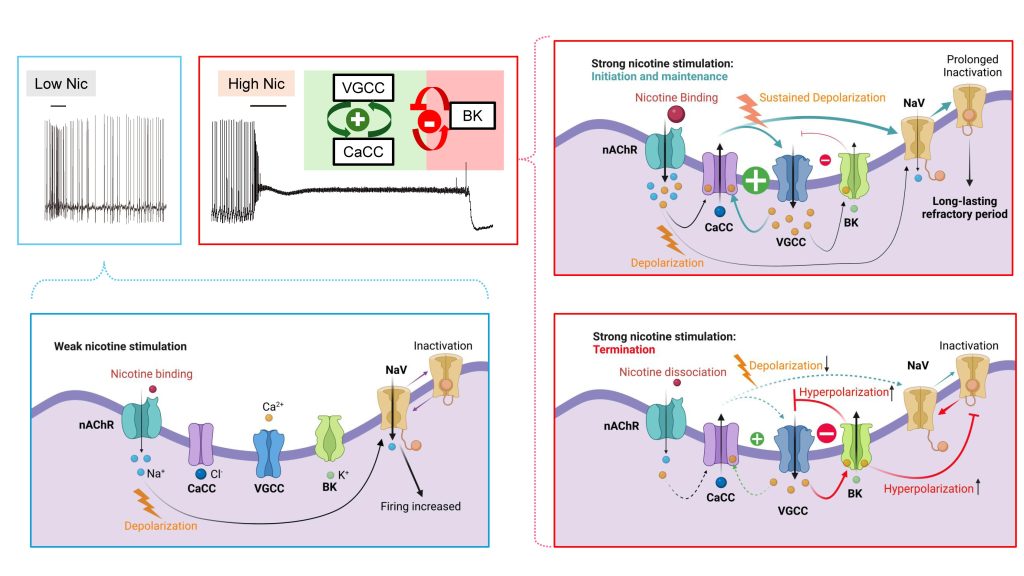
B. Calcium-activated lipid scramblases
- TMEM16F, a calcium-activated ion channel and lipid scramblase, plays a critical role in blood coagulation (Yang, et al, Cell, 2012)
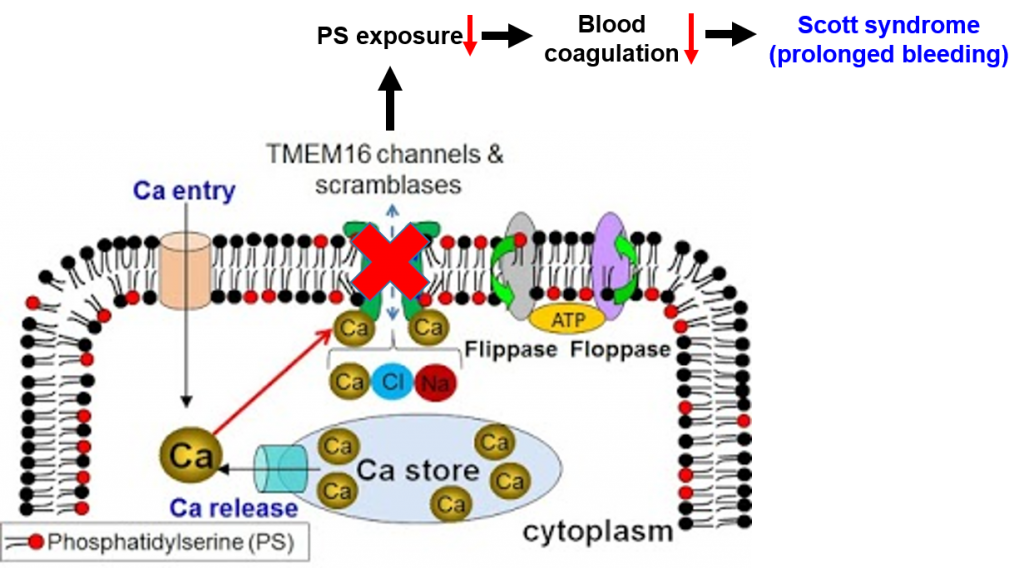
- TMEM16F-mediated phosphatidylserine exposure is critical for placental trophoblast fusion and placental development. (Zhang et al. Sci. Adv., 2020)
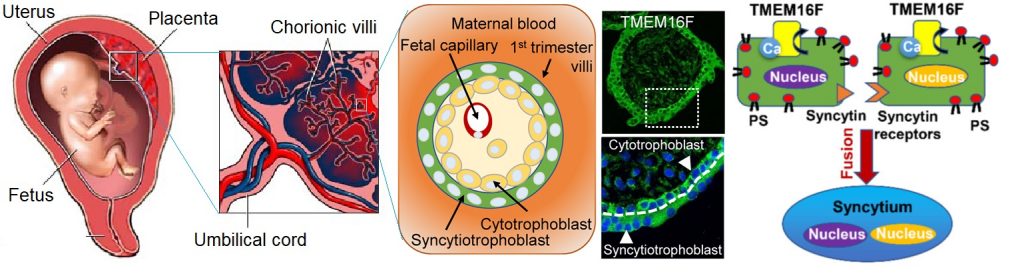
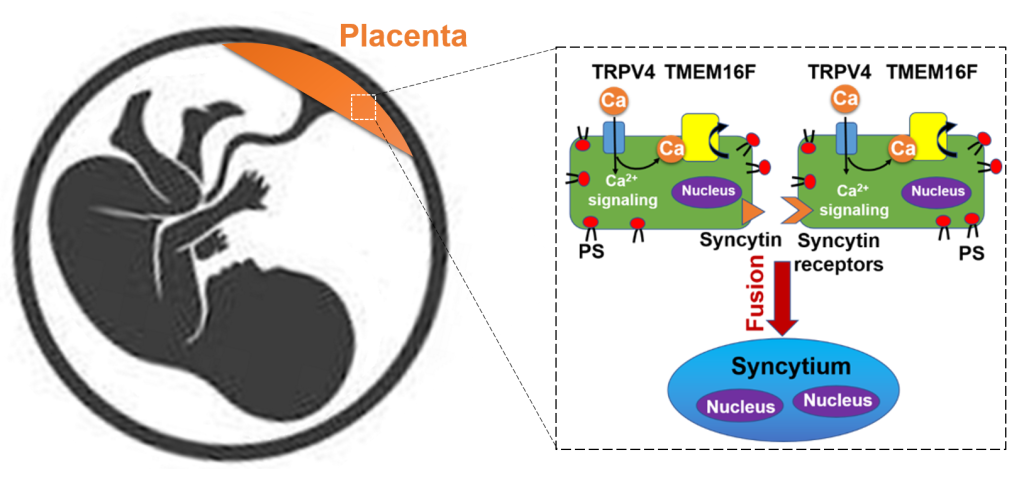
- Discovered placental TRPV4 that regulates TMEM16F activation and trophoblast fusion. (Yang et al, eLife, 2022)
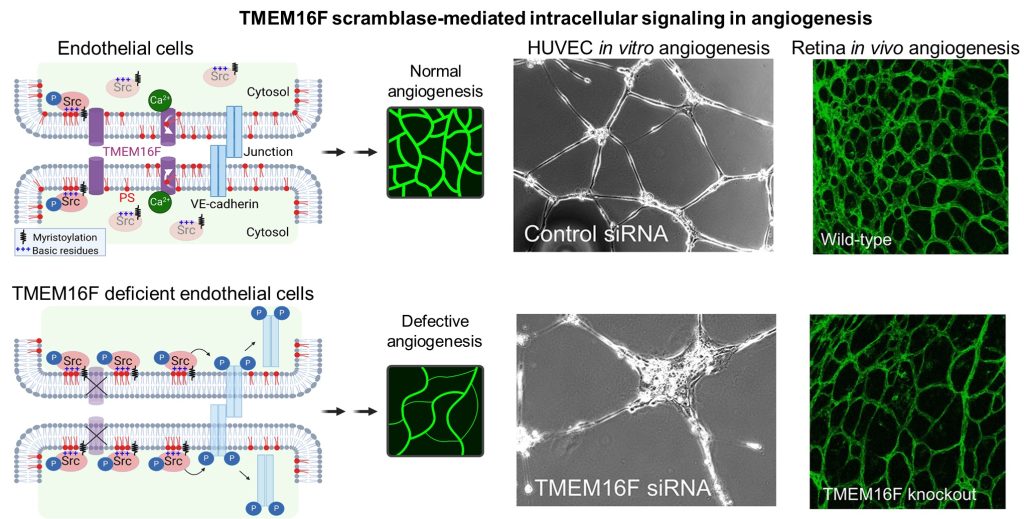
- Discovered an intracellular signaling role of TMEM16F lipid scramblase in endothelial cells and angiogenesis. (Shan et al, J. Cell Sci., 2024). Also see the interview with the first authors.
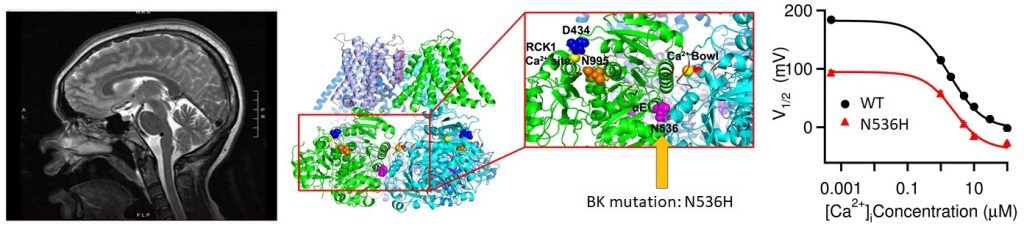
C. Calcium-activated BK channels
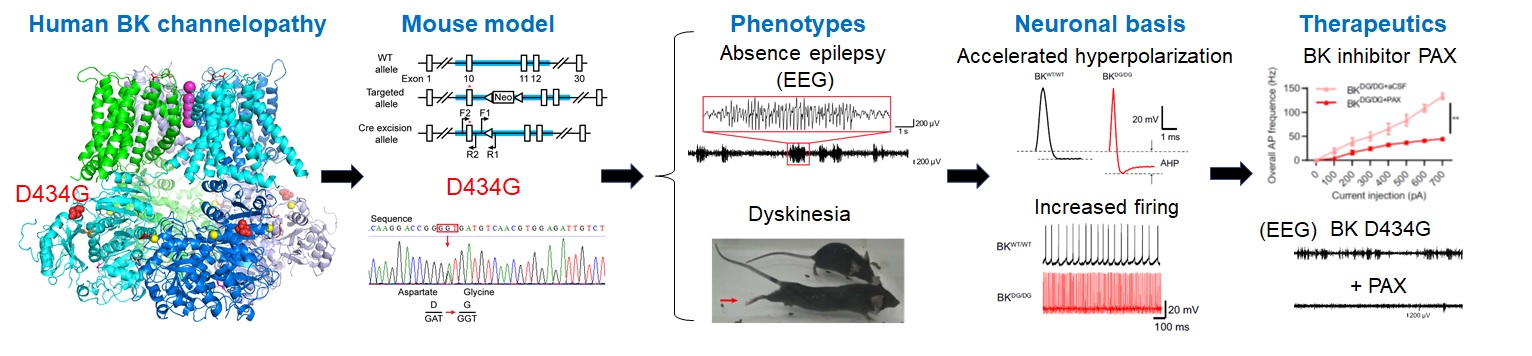
- Seventeen years after discovering the D434G mutation in the BK channel linked to absence seizures and dyskinesia, we studied it using a knockin mouse model. This model mirrored clinical symptoms, revealed neuronal bases, and suggested a therapeutic approach for the channelopathy. (Dong, et al, PNAS, 2022).
- Collaborating with the Mikati lab and the Cui lab, we identified and characterized a novel BK gain-of-function mutation that causes dystonia (Zhang, et al, Mov. Disord. , 2020)
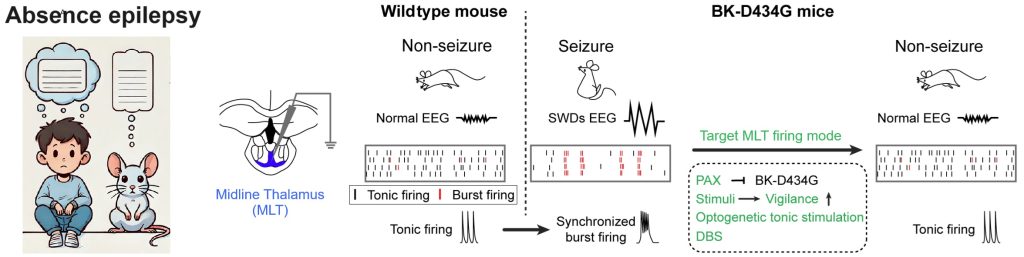
- We discovered the critical role of midline thalamus (MLT) neurons in absence epilepsy, showing that their synchronized burst firing, driven by enhanced BK channel activity, is pivotal for seizure occurrence. We demonstrate that interventions targeting MLT neurons, including optogenetic, electrical, or pharmacological methods, significantly reduce seizure frequency in the BK channelopathy mouse model, positioning the MLT as a promising target for new therapeutic strategies (Dong, et al, PNAS, 2024)
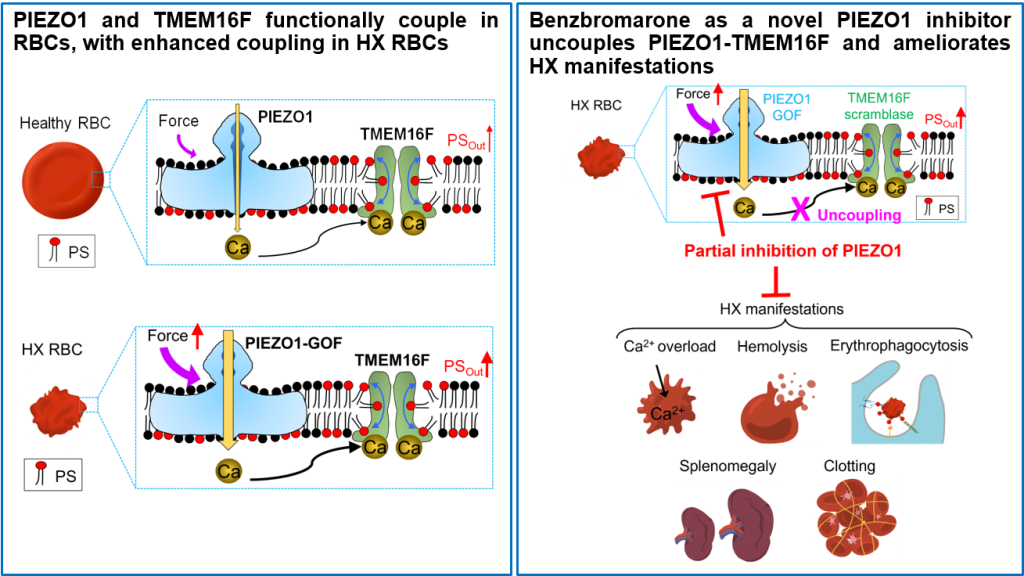
- Deciphering and disrupting PIEZO1-TMEM16F interplay in Hereditary Xerocytosis (HX), a rare red blood disorder (Liang, et al, Blood, 2024). See Commentary here.
- First discovery of PIEZO1 mechanosensitive channel in controlling trophoblast fusion and placental development (Zhang et al, Nat. Commun., 2025). See Research Highlight and Biomedical Picture of the Day

3. How can we target ion and lipid transport pathways for therapeutic development?
-
-
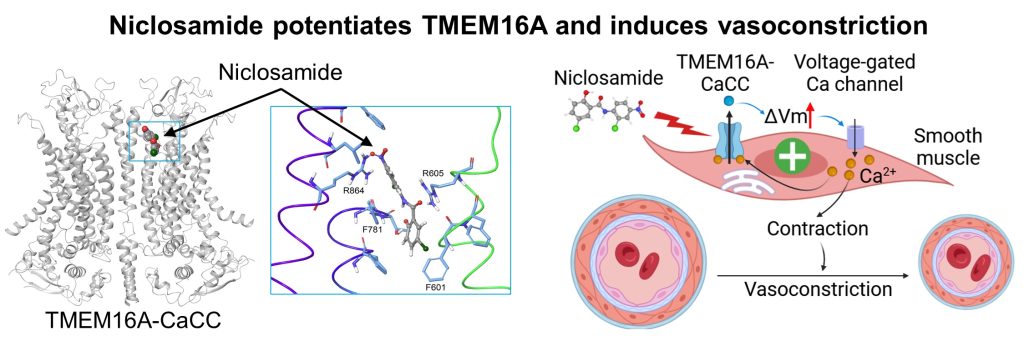
- Niclosamide potentiates TMEM16A and induces vasoconstriction (Liang, et al, JGP, 2024)
- Breaking PIEZO1-TMEM16F coupling as a novel strategy to reduce sickle cell disease complications (Liang, et al, Am. J. Hematol, 2025)
-
4. Method development
-
-
- An optimized fluorescence imaging assay to quantify lipid scrambling (Le, et al, JBC, 2019)

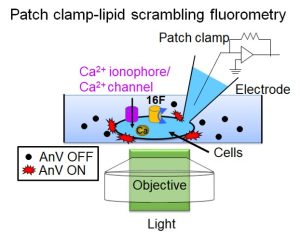
- A patch clamp-lipid scrambling fluorometry (PCLSF) method to quantify the dual functional TMEM16 scramblases and channel (Liang and Yang, J. Gen. Physiol. 2020).
- An optimized fluorescence imaging assay to quantify lipid scrambling (Le, et al, JBC, 2019)
-
-
-
-
- A simple and economic method to quantify cell-cell fusion index (Zhang & Yang,, Placenta, 2019).
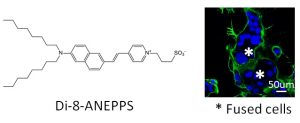
- A simple and economic method to quantify cell-cell fusion index (Zhang & Yang,, Placenta, 2019).
-
-