Retinal laser therapy is an ophthalmologic procedure that requires the doctor to seal or destroy leaking blood vessels in the retina with a laser, commonly treated for patients with diabetic macular edema. This procedure involves a magnifying lens to inspect the retina, bringing challenges of prolonged training and dealing with an inverted image. To address this challenge, we developed an Augmented Reality-based training tool that provides in situ guidance with a direct overlay on the magnifying lens for microsurgical ophthalmic tasks in indirect ophthalmoscope retinal laser therapy.
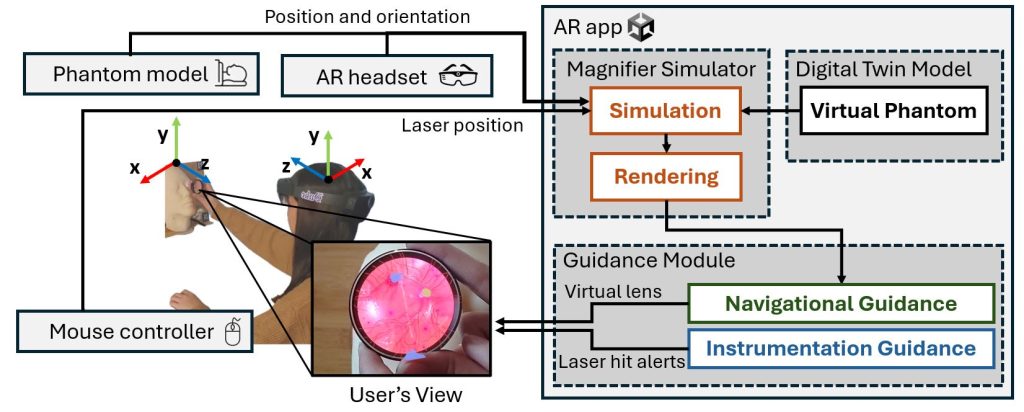
Our architecture contains three hardware components: 1) sensor, 2) edge server, and 3) AR headset. The camera sensor captures the magnified image through the magnifying lens and sends it to the edge server over a wireless local area network. The edge server then, enhances the images to produce more “feature-rich” images, computes the feature points on both magnified and reference images (i.e., a pre-taken image that entails the shape and size of the whole object), and matches the feature point for homography matching between the magnified image and the reference image.

We first evaluated our system with a general object, a keychain with the Duke University logo to demonstrate the AR magnification. During this demo, the participants can move the keychain up or down, and left or right, to update its location to follow the movement. The participants can also move the keychain forward and backward to update its scale to reflect the change in magnification.
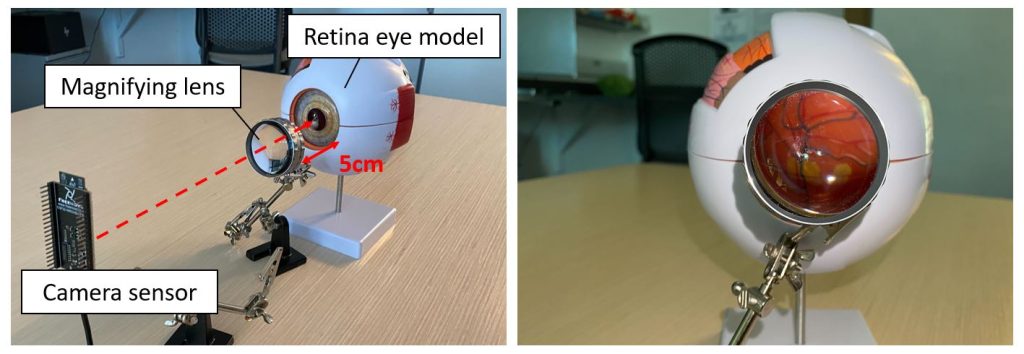
We plan to implement our system on retinal laser therapy using a color fundus image to magnify and visualize the anatomical landmarks (e.g., blood vessels, macula, optical disc) on the magnifying lens to guide the doctors. We will further integrate the AR-based guidance that allows doctors to identify the region that needs to be treated and alert on not hitting the landmarks to maximize the safety of patients and the efficiency of the retinal laser therapy.
A link to the demo video can be found here: https://sites.duke.edu/sangjuneom/arglass
Grants
Duke Eye Center Research to Prevent Blindness Small Grant (Funding: $3,000), 2023
Media Coverage
Duke PhD Student Presents Research on Utilizing AR Guidance System in Retinal Laser Therapy, Duke Eye Center News, May 2023 [Link]
2023 VISION Magazine, Duke Eye Center News, July 2023 [Link]
Related Publications
Improving laser targeting accuracy with Augmented Reality guidance in retinal laser therapy [Link]
S. Eom, M. Pajic, M. Gorlatova, M. Hadziahmetovic.
In Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 65, No. 7, May 2024.
Demo Abstract: Edge-based Augmented Reality Guidance System for Retinal Laser Therapy via Feature Matching [Link][Video]
S. Eom, R. Janamsetty, M. Hadziahmetovic, M. Pajic, M. Gorlatova.
In IEEE/ACM International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Network (IPSN, co-located with CPS-IoT Week), May 2023.
Augmented Reality for Retinal Laser Therapy [Link]
S. Eom, M. Pajic, M. Gorlatova, M. Hadziahmetovic.
In Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 64, No. 8, April 2023.
Demo Abstract: Through an AR Lens: Augmented Reality Magnification through Feature Detection and Matching [Link][Video]
S. Eom, M. Hadziahmetovic, M. Pajic, M. Gorlatova.
In ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems (SenSys), Nov. 2022.
Current Team Members
Sarah Eom, ECE, Duke University (Primary)
Dr. Majda Hadziahmetovic, Duke Ophthalmology
Dr. Maria Gorlatova, ECE, Duke University
Dr. Miroslav Pajic, ECE, Duke University
Tiffany Ma, Undergraduate in CS, Duke University
Former Team Members
Alex Meng, Undergraduate in CS, Duke University