Modelling Study of Global Trends in
Vaccine Confidence
Author: Reika Shimomura
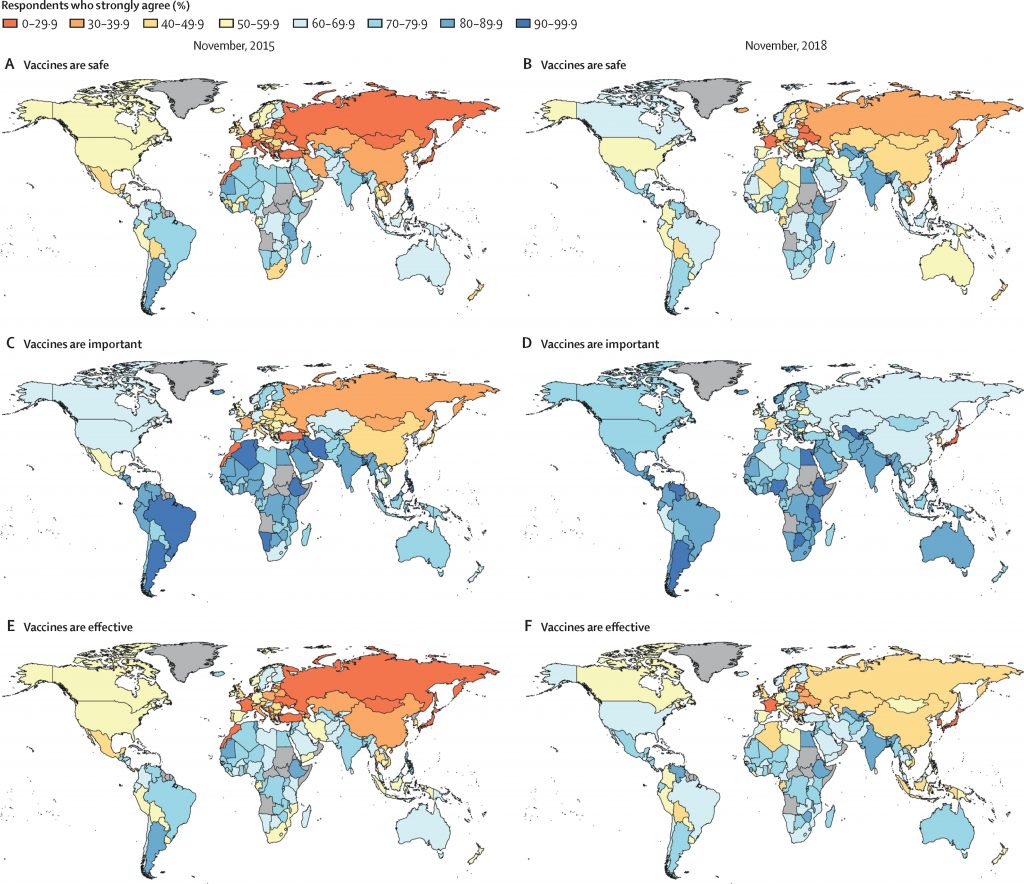
Instead of focusing on the coverage of vaccinations, this modelling study examines the change in vaccine confidence among 149 countries over a time period from 2015 to 2019 (Figure 1). The trends of vaccine confidence across the countries are shown through anon-parametric model with multiple classifications of safety, importance, and effectiveness of vaccines. The survey respondents answered either “strongly agree” or “strongly disagree” in these three classifications of vaccine confidence. The recognition of change in the vaccine confidence level highlights the possible determinants of vaccine uptake. For example, from Figure 2, Japan had the lowest vaccine confidence compared to the other countries, which may be associated with the public’s questioning of the safety of the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine which started in 2013.
Similar events may have negatively associated with the chances of uptake such as misinformation on vaccination spread online in South Korea and Malaysia, and intense media coverage in Georgia. There could also be an association with religious reasons especially for Indonesia, which had a large drop in confidence during this period among Muslims. Such misinformation and controversy between different interest groups largely affected the vaccinations of measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR). This finding on the vaccine confidence would be valuable context for the uptake of COVID-19 related vaccines soon.
References:
Figure Retrieved from Figueiredo, A. D., Simas, C., Karafillakis, E., Paterson, P., & Larson, H. J. (2020). Mapping global trends in vaccine confidence and investigating barriers to vaccine uptake: A large-scale retrospective temporal modelling study. The Lancet, 396(10255), 898-908. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31558-0
Mapping global trends in vaccine confidence and investigating barriers to vaccine uptake: a large-scale retrospective temporal modelling study. The Lancet. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)31558-0/fulltext