Comparison of Analysis Strategies for COVID-19 Mass Testing
Author: Reika Shimomura
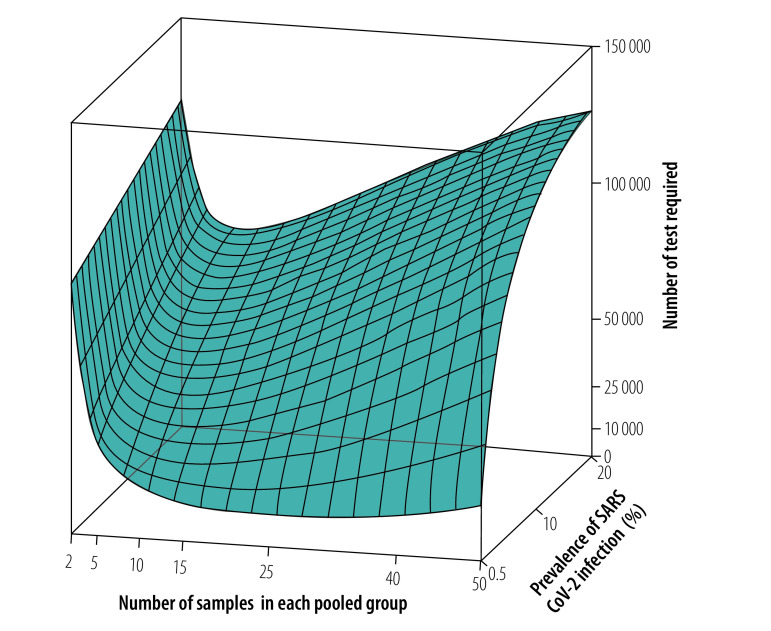
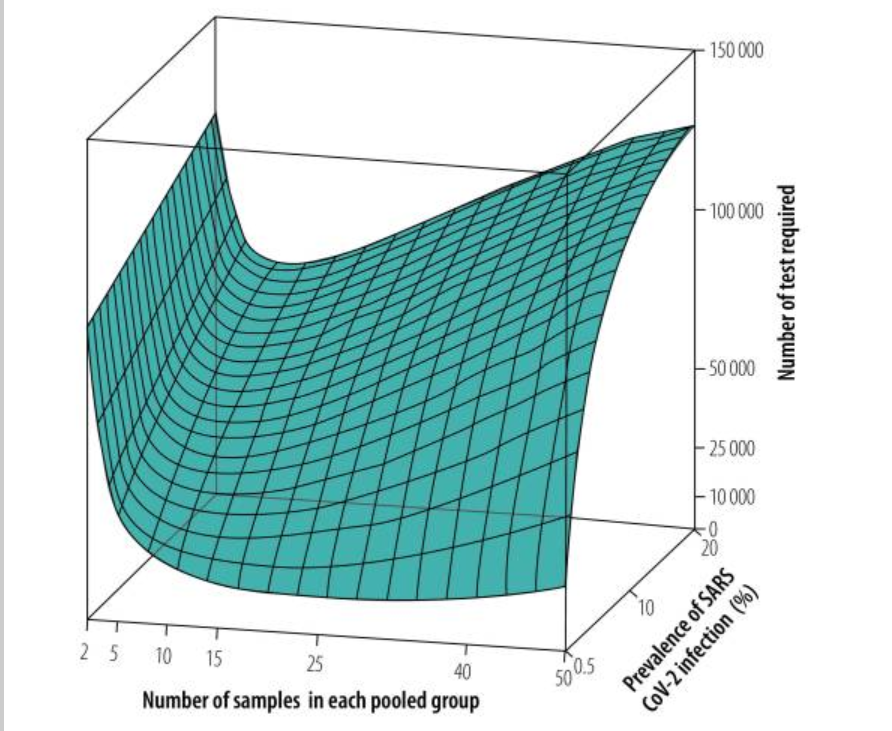
Simulation visualizing the results of pooled-sample analysis strategies with three variables: number of samples in each pooled group, prevalence of SARS CoV-2 Infection (%), and number of tests required. The left graph shows the high-throughput approach and the right graph shows the context-sensitive approach.
Pooled-sample analysis is used for COVID-19 and other diseases that require mass testing – this analysis style improves the efficiency and saves the resources of diagnostic tests compared to individual analysis. In this paper, two strategies of pooled-sample analysis are compared with Monte Carlo simulations to visualize outcomes with different parameters. The main parameters considered in this paper are: test resources (measured by the number of tests required) and prevalences of SARS CoV-2 infection. One strategy is “a routine high-throughput approach” where polymerase chain reaction (PCR; a diagnostic test for COVID-19) is carried out in randomized heterogenous sample pools and the other is “a novel context-sensitive approach” which performs the PCR with homogeneous groups of samples. The simulation results of each strategy can be compared in Figure 4 and Figure 5. Although both strategies are cost-effective, the results show that the novel context-sensitive approach requires substantially fewer tests, even if the prevalence of infection of the population is increased up to 20%. This information would contribute towards the development of a suitable approach in the setting of outbreaks or before the second-wave of an outbreak.
References:
Figure retrieved from: Deckert A., Barnighausen T., and Kyei N. et al., Simulation of pooled-sample analysis strategies for COVID-19 mass testing, doi: 10.2471/BLT.20.257188
Article Title: Simulation of pooled-sample analysis strategies for COVID-19 mass testing https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7463190/