Wet granular rafts
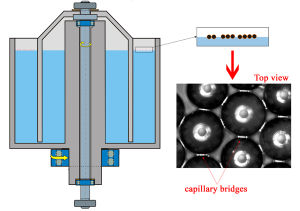
Shearing is widely used in industries such as chemical engineering, mining and waste water treatment. For the particles (200 micrometer in diameter) trapped at the air-liquid interface, the forces acting on them usually include mono-polar forces (gravity, buoyancy force), dipolar forces (due to the electric charge between the interface) and quadrapole force (capillary interaction due to the distortion of liquid interface). Here we introduce a hysteretic and short ranged attractive force by using a second liquid which is immiscible with the bulk liquid to wet particles and form liquid bridges between them. In such a way we create a 2D wet granular media. By applying a shear force, we study the aggregation of 2D wet granular material.
Comparison between dry and wet sample under shear (as the two sample videos shown below) indicates that the capillary force dominates the others. For dry sample, particles aggregation due to the quadrapole force could easily be broken by the viscous drag force. While at the same shear rate, the aggregation formed by wet sample persists.
Video:2D dry glass spheres under shear.
Video:2D wet glass spheres under the same shear rate.
The movement of particles under shear flow is captured by a high speed camera and the images captured are in turn subjected to image processing which enables tracing of individual particles. After image processing, we could get the location, velocity and corresponding cluster index of all the particles found in the field of view, based on which the location, velocity, equivalent diameter, orientation of the clusters could be obtained. Below is a video clip after image processing. The particles are color coded by which cluster they are belonging to.
Video:2D wet glass spheres under the same shear rate, after image processing.
With this setup, the formation, growing and merging of clusters as well as its dependence on the driving shear force are studied and compared to numerical simulations. We also study the cluster size distribution and its dependence on shear rate and the fractal dimension of the clusters formed at different shear rate. Further study will focus on the high area fraction regime and study the melting, jamming and rigidity of 2D wet granular matter under shear.
Video:2D wet glass spheres under shear, original video.
Video:2D wet glass spheres under shear, video after image processing.
Reference
- “Wet granular rafts: agglomeration in two dimensions under shear”, Kai Huang, Martin Brinkmann and Stephan Herminghaus, Soft Matter 8, 11939 (2012), doi:10.1039/C2SM26074C